We will create a git repository to host our code.
Prepare .gitignore file
We will create a .gitignore file that contains files that should not be tracked.
gitignore.io creates a .gitignore file according to the technologies used in the project.
Open gitignore.io in your browser, add the terms intellij, macos, sbt and scala and click create.
This will generate the content of a .gitignore file with predefined files/directories.
Open the .gitignore file in your project dir, e.g ~/repos/playground/.gitignore, and copy the content from the site to the file.
Add .g8/ to the .gitignore file as the first line (or remove the gitter8 directory, which is no longer needed, by running rm -rf .g8/ in your terminal).
Add .idea/ to the .gitignore file. This directory contains IntelliJ Idea settings and should not be committed to git.
Initialize a git repository
In the project directory in your terminal, type git init.
This will create a new hidden directory called .git inside your project directory.
Commit our work
See untracked files by typing git status.
Let’s run git add . to stage all the files to commit.
Type git status again to see that your files are now staged for commit.
Commit the staged files by running: git commit -m "initial commit".
The changes were committed in your local repository.
You can see with git status that we have nothing new to commit.
Running git log will show your commit, and show that HEAD points to master.
Now we will add a remote repository and push our changes.
Create a remote repository
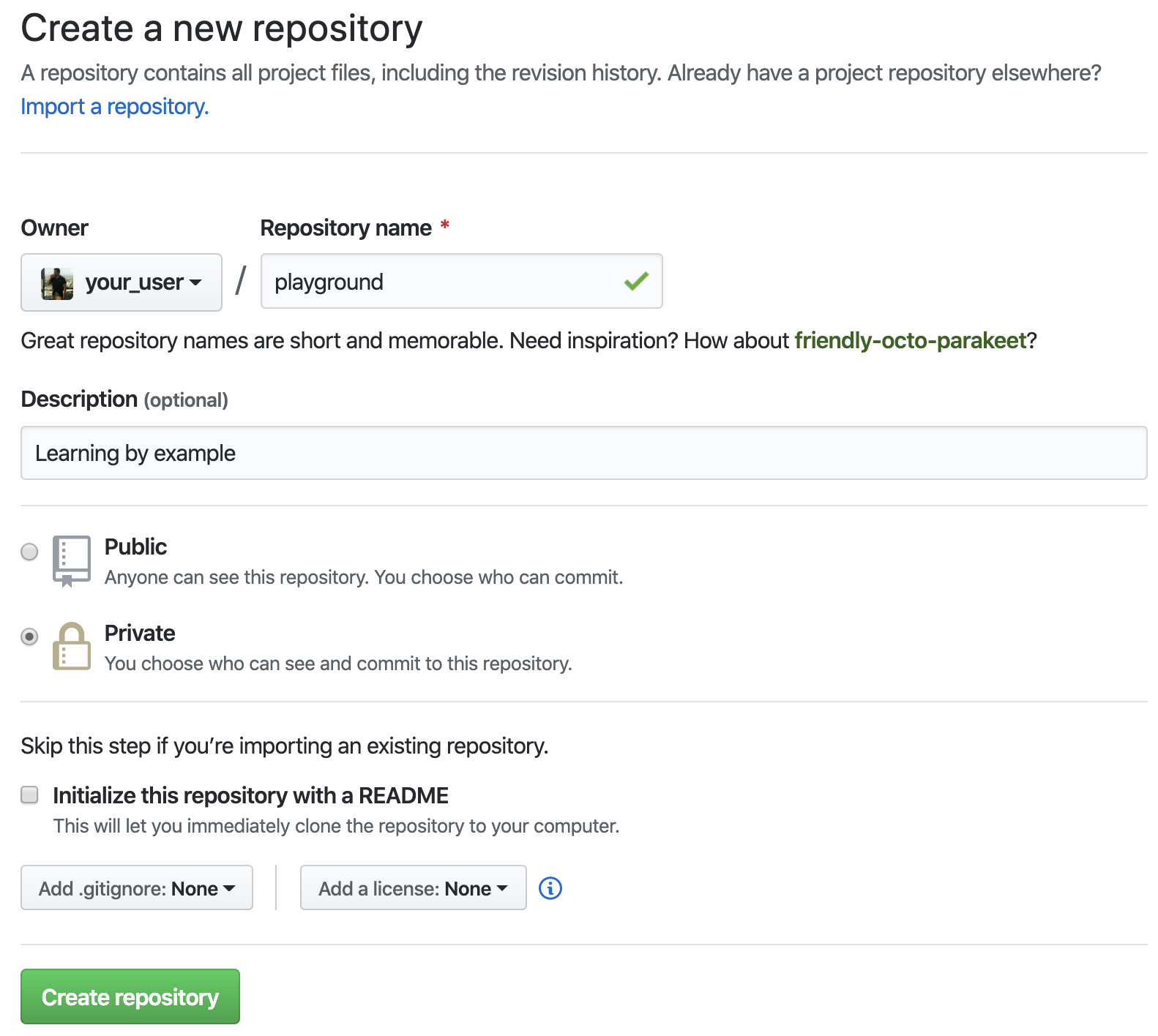
Let’s create a new github (remote) repository:
Browse to GitHub, click the + (create) button, and click New repository.
Fill out the following:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Owner | <your user> |
| Repository name | playground |
| Description | Learning by example |
| Access Level | Private |
| Initialize this repository with a README | No |
| Add .gitignore | None |
| Add a license | None |
And click Create repository.
Add a remote
Instructions to add this new remote, which will be called origin to your local repository (called master) will appear on the screen.
In your project directory in your terminal, run:
git remote add origin git@github.com:<YourUser>/playground.git and push the commits from the local master branch to the remote origin by running:
git push -u origin master.
Refresh the github tab in your browser to see your code there.
Run git log again and see that HEAD now points to master and origin/master.